This post will give you an overview of what happens whenever you try to access a web page through a web browser...
Whenever you entered a URL such as www.google.com into your web browser, the browser sends a request to DNS in order to translate the beautiful and easily remembered URL (google.com) into the IP Address (e.g 127.243.753.12) of the server in which the web page is stored. When the IP is identified, a TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) is established. This ensures that data is transmitted successfully and efficiently between your device and the server it is trying to access.
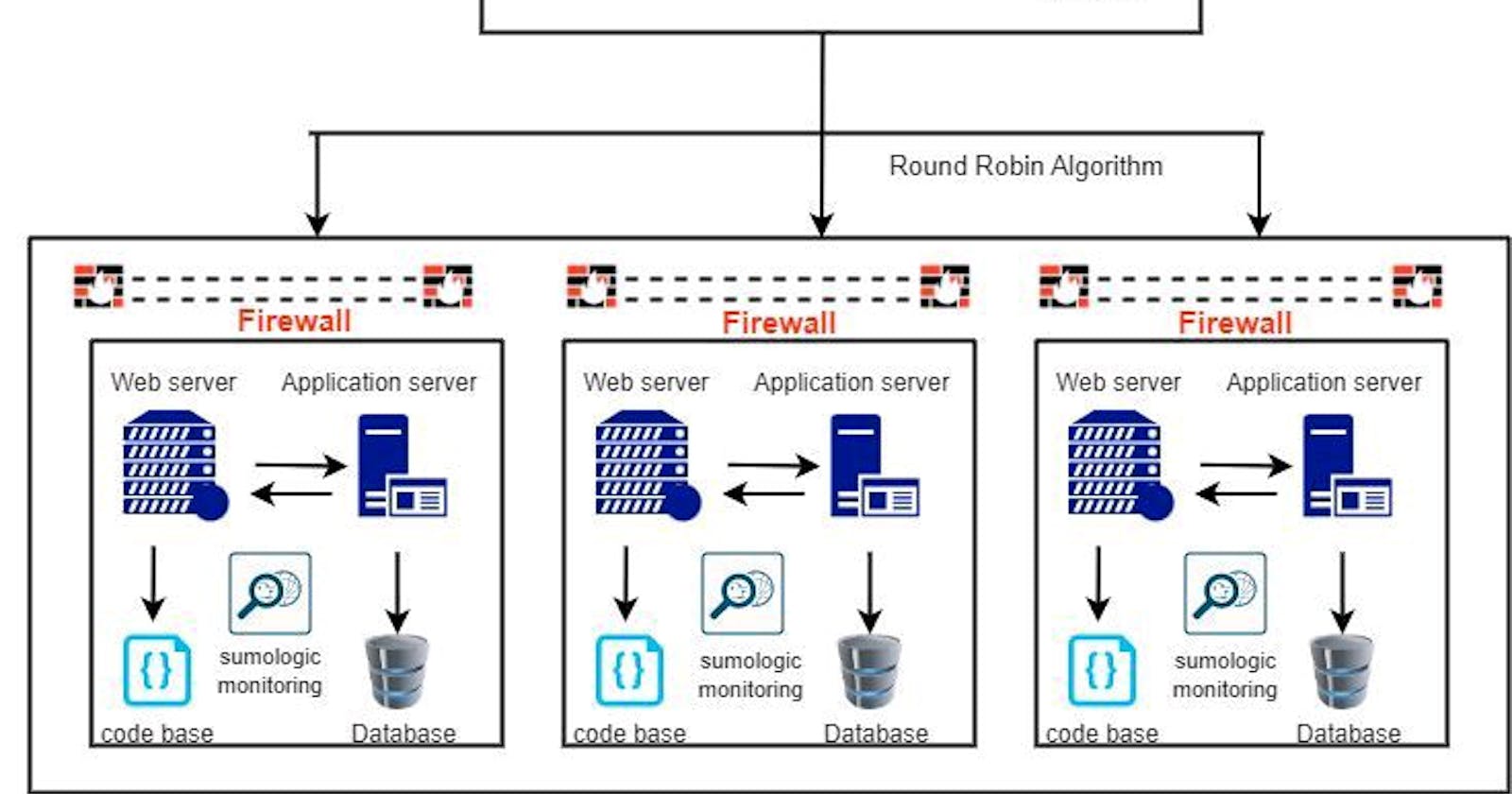
The moment a TCP/IP connection is made, the next is the FIREWALL (which checks for incoming and outgoing network traffic based on certain set of rules) which will check if the request is allowed through to the server.
Once the request is cleared by the FIREWALL, your request will be sent to the LOAD BALANCER which will distribute network traffic among other servers (2 or more) so that a single server will not be overloaded with traffic which might cause a server break down or SPOF (single point of failure).
After passing through the LOAD BALANCER, the request will be sent to the web server which will handle your request and server the necessary css, html and javascript needed to make up the website.
The web server then sends the request to the application server, which is responsible for executing any server-side code and querying the database to retrieve any necessary information.
When that is done, the application server sends the request to the database, which retrieves the requested data and sends it back to the application server. The application server then formats the data and sends it back to the web server, which returns it to the user's browser to be displayed as the Google website.
It's also important to note that, the request is using HTTPS (HTTP Secure), a security protocol that encrypts the transmitted data, adding an extra layer of security to the process. The SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate which is used to encrypt the traffic is also verified by the browser.