Linear Regression is an essential machine learning algorithm used in various applications today. It works by finding the relationship between a variable or target and one or more data points also known as features by fitting linear equations on the data points. As a machine learning engineer or an aspiring machine learning engineer, you will most possibly find yourself using this algorithm on a day-to-day basis to solve some machine learning problems. In this article, I will be walking you through a step-by-step process on how to implement this same algorithm yourself from scratch using Python. We will also be exploring the linear algorithm intuition so you can understand the mathematical equations behind this powerful algorithm.
lets dive in ...
What is linear Regression?
Linear regression is an algorithm that aims to find the best fit linear relationship between an independent variables(features) and a dependent variable(target). It is denoted by this formula:
y = wx + b
where:
w = parameters (weights)
b = Bias (parameters)
X = features
the goal is to find the parameters w and b that will best fit the data.
How does linear regression works?
Linear regression works by multiplying the weights and the features plus the bias and constantly updating the parameters till the cost J(X) is minimized
Cost Function
Since the goal in linear regression is to find the best line that fits the data, the cost function is the metric used to measure how well the model is performing. This is done by calculating the difference between the predicted value and the actual value.
In linear regression, the popular cost function used is "Mean Squared Error Cost Function"
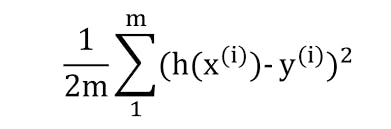
where h(x) is the predicted value ^y gotten using the linear function y = wx + b across all training examples
y = the actual value
m = the number of training examples
and by constantly optimizing the value of weights and bias, we can minimize the cost function and therefore increase the model accuracy.
Gradient Descent
One very fascinating question is that, "how do we optimize the parameters?". Well, this is done by iterating n number of times, and for each iteration, we take the derivative of the cost J(X), subtract it from the learning rate and updating the parameter with it
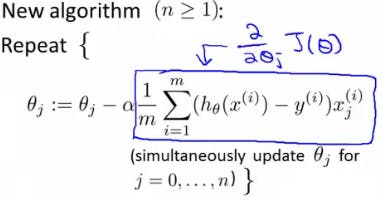
I know it sounds confusing,
theta(j) is the parameter weights
alpha = the learning rate, it can be a constant value.
Linear Regression in Python code
import numpy as np
class LinearRegression:
def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.01, iter=1000):
self.lr = learning_rate
self.iter = iter
self.weights = None
self.bias = 0
def fit(self, X, y):
n_sample, n_feature = X.shape
self.weights = np.zeros(n_feature)
y_pred = self.predict(X)
for _ in range(self.iter):
self.weights = self.weights - self.lr * np.dot(
X.T, y_pred - y)
self.bias = self.bias - self.lr * np.sum(y_pred - y)
def predict(self, X):
y_pred = np.dot(X, self.weights) + self.bias
return y_pred
e
import numpy as np: This line imports the NumPy library and aliases it as np. NumPy is used for numerical computations, and it's a fundamental library for data manipulation in Python.
class LinearRegression:: This defines a Python class namedLinearRegression, which is used to encapsulate the linear regression model and its methods.def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.01, iter=1000):: This is the constructor method for theLinearRegressionclass. It initializes the class attributes:learning_rate: This is the learning rate for the gradient descent optimization algorithm, which determines the step size during the weight and bias updates. The default value is set to 0.01.iter: This is the number of iterations for which gradient descent will run during model training. The default value is set to 1000.weights: This attribute represents the coefficients (weights) of the linear regression model.bias: This attribute represents the bias term of the linear regression model.
def fit(self, X, y):This method is used to train the linear regression model. It takes two parameters:X: The input features or independent variables.y: The target variable or dependent variable.
Inside this method:
It calculates the number of samples (
n_sample) and the number of features (n_feature) in the input data.Initializes the
weightsattribute as an array of zeros with a length equal to the number of features.Predicts the target variable (
y_pred) using thepredictmethod (which is expected to be defined elsewhere in the class).It performs gradient descent to update the
weightsandbiasiteratively based on the prediction error (the difference betweeny_predandy) and the learning rate.
def predict(self, X):: This method is used to make predictions using the trained linear regression model. It takes the input featuresXas a parameter and returns the predicted valuesy_pred. Inside this method:It calculates the predicted values
y_predby performing a dot product between the input featuresXand the model'sweights, and then adds thebiasterm.Finally, it returns the predicted values.
Linear regression is absolutely an essential and interesting algorithm to use as a machine learning engineer.
With this model, you can now solve any supervise learning problem, Also, note that this implementation of linear regression is quite simple and might need some optimization method to help it predict more accurate value.
Thanks for reading