How a DNS server works?
An 8-step guide on how a DNS server works under the hood
If you have always wondered how a DNS server works, this post will give you an overview of how DNS works under the hood 😎 .
First, what is DNS?
DNS (Domain Name System) is the system that translates domain names, such as www.google.com, into IP addresses, which are numerical labels used to identify devices connected to the internet.
But you might be wondering how DNS works in a nutshell
This 8-step process will give you an overview of how it really works:
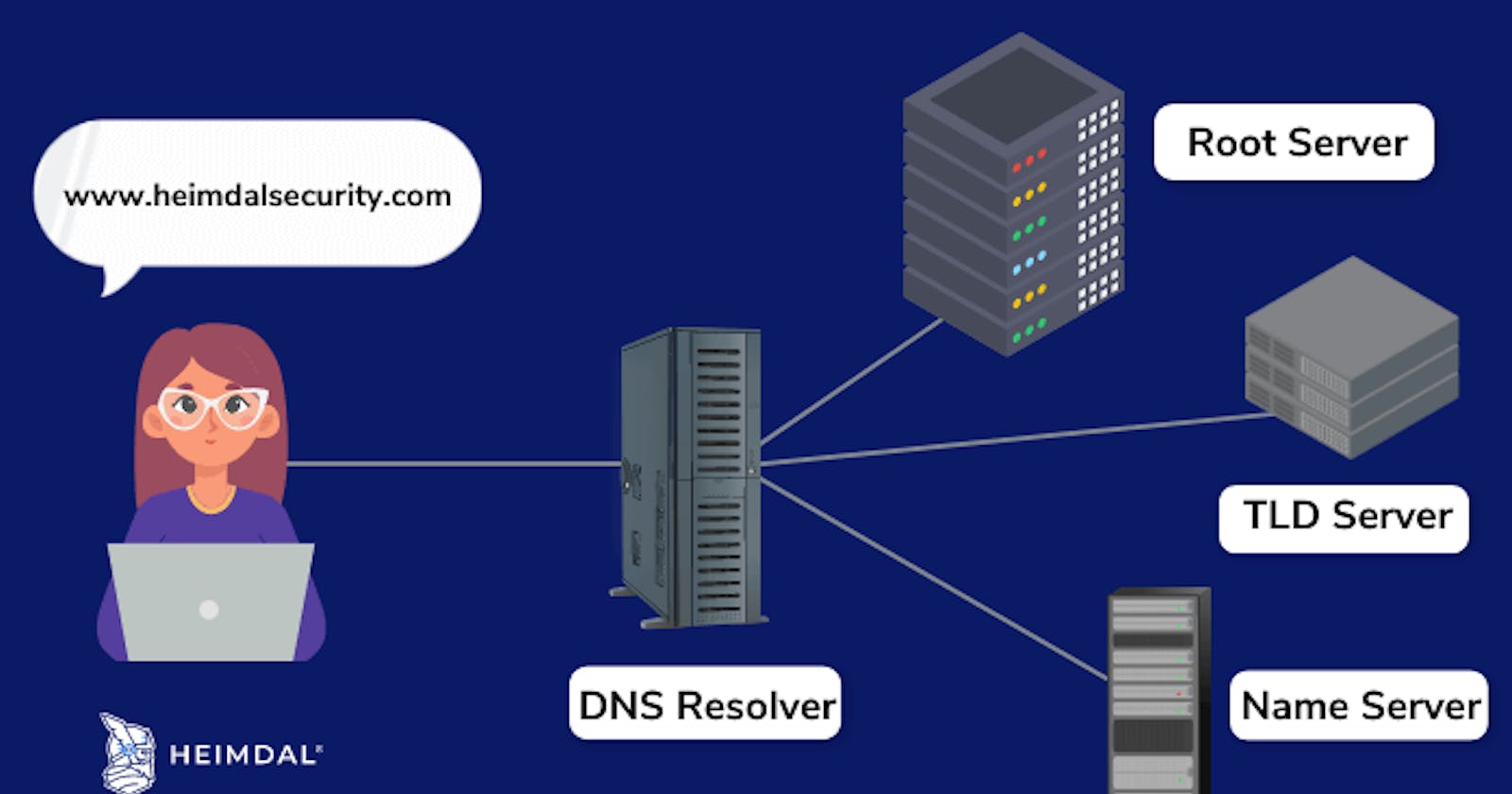
1. A user types a domain name into their web browser or clicks on a hyperlink that points to a domain name.
2. The user's computer sends a request to a DNS resolver, which is typically provided by the user's Internet Service Provider (ISP).
3. The DNS resolver queries a series of DNS servers, starting with the root DNS server, to determine the IP address associated with the domain name.
4. The root DNS server returns a referral to a top-level domain (TLD) DNS server, such as .com, .org, .net, etc.
5. The TLD DNS server returns a referral to an authoritative DNS server for the specific domain name being queried.
6. The authoritative DNS server returns the IP address associated with the domain name to the DNS resolver.
7. The DNS resolver returns the IP address to the user's computer.
8. The user's computer can then establish a connection to the IP address and retrieve the content associated with the domain name.
This process usually takes place in a matter of milliseconds and happens transparently in the background, allowing users to access websites and other online services by using domain names instead of having to remember IP addresses.