As the world becomes more interconnected and the demand for seamless communication between different applications and services continues to grow, the need for well-designed APIs and RESTful web services becomes increasingly important. In this beginner's guide, we'll explore what RESTful web services are, how they work, and best practices for designing effective APIs.
What are RESTful Web Services?
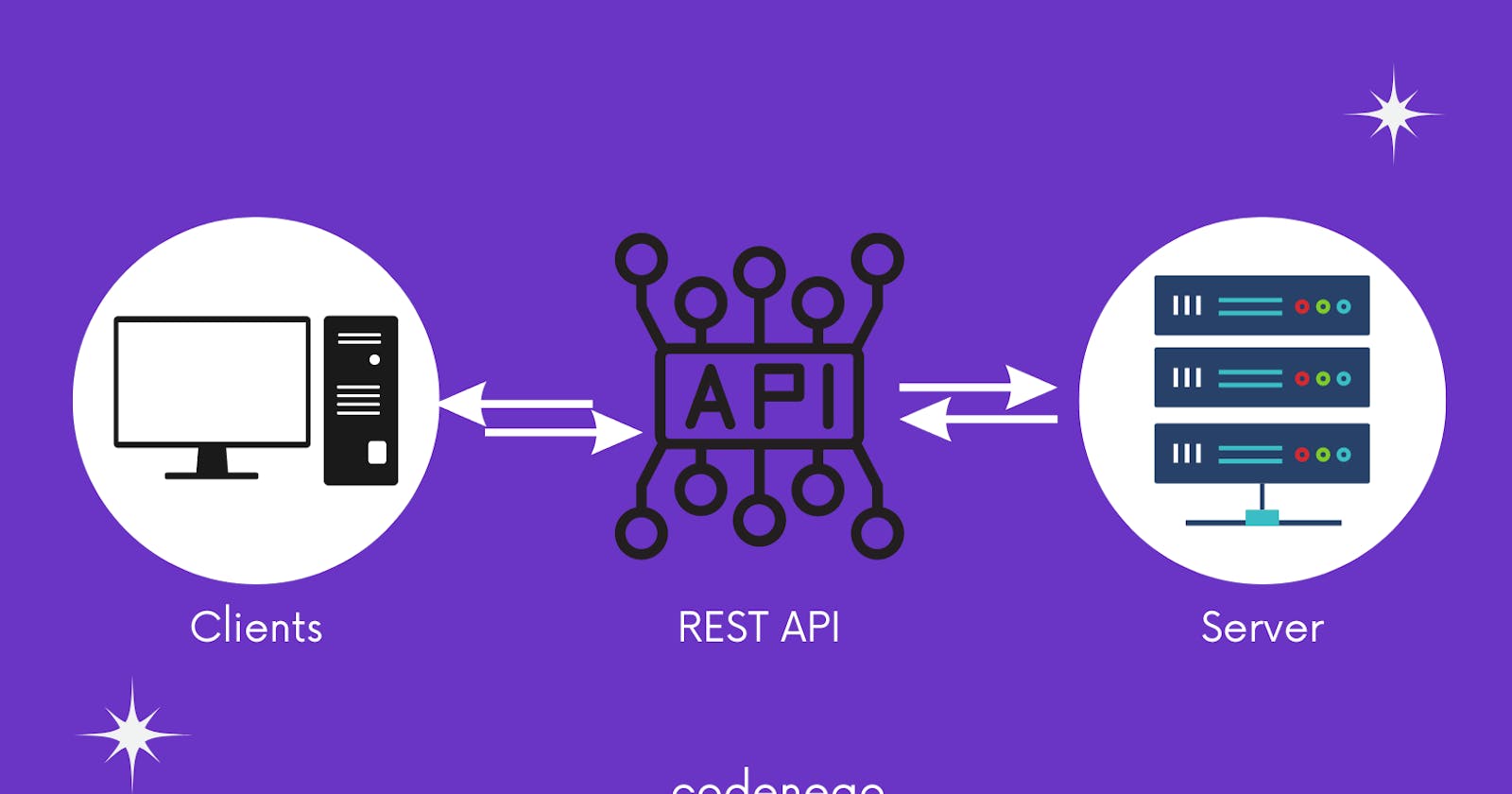
REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style for building web services. A RESTful web service is a web service that follows the REST architecture, which means it uses HTTP protocols for data transfer and resource access. RESTful web services are designed to be simple, lightweight, and easy to use, and they are the most popular way of building APIs today.
RESTful web services are based on the concept of resources. In REST, a resource is an object or data entity that is accessed through a unique URL or endpoint. The basic operations that can be performed on a resource are represented by HTTP methods, such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. For example, to retrieve information about a user, we might send a GET request to the /users/{id} endpoint.
How Do RESTful Web Services Work?
At a high level, the flow of data in a RESTful web service follows a client-server architecture. The client sends an HTTP request to the server, which processes the request and sends a response back to the client. The response typically contains data in a specific format, such as JSON or XML, that the client can understand.
The key features of a RESTful web service are:
Stateless: Each request sent to the server must contain all the necessary information for the server to process it. The server does not store any client data between requests.
Uniform Interface: RESTful web services use a uniform interface for all interactions between clients and servers. This includes the use of HTTP methods for different operations, such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE, and the use of unique URLs for each resource.
Cacheable: RESTful web services can be designed to be cacheable, which can help reduce network traffic and improve performance.
Layered: RESTful web services can be layered, meaning that the client interacts with a proxy or gateway server that forwards the request to the actual server.
Best Practices for Designing RESTful Web
To ensure that your RESTful web services are efficient and user-friendly, it is important to adhere to the following guidelines:
- Implement resource-oriented URLs that are easy to comprehend and have a coherent structure. Avoid query parameters in the URL unless they are absolutely necessary.
Use HTTP Methods Correctly: Use HTTP methods correctly for different operations, such as GET for retrieving data, POST for creating new resources, PUT for updating existing resources, and DELETE for deleting resources.
Use Standard Status Codes: Use standard HTTP status codes to communicate the status of a request, such as 200 for a successful response, 404 for a not found response, and 500 for a server error response.
Use a Consistent Data Format: Use a consistent data format, such as JSON or XML, for data transfer between the client and server. This makes it easier for clients to parse the response and for developers to work with the API.
Implement Pagination: If you're returning a large set of data, it's best to implement pagination so that the client can request a specific page of data. This helps to improve performance and reduce network traffic.
Version Your APIs: When making changes to your API, it's important to version it so that existing clients can continue to work with the old API while new clients can use the new API.
Use SSL/TLS for Security: Use SSL/TLS to secure communication between the client and server, and make sure to use secure passwords and access control mechanisms
To round this post up, as a beginner, it is important to follow best practices for resource-oriented URLs, HTTP methods, status codes, data formats, pagination, API versioning, and security. By following these best practices, you can create effective and easy-to-use APIs that meet the needs of your clients and users.
Do you want understand what happens when you type google.com in your browser?
check out this post below, it will give you a better insight.